![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
In
this section there are enclosed quotations from official technical reports
concerning five main dredging jobs carried out for environmental reclamations,
in four different areas of the world (Japan, U.S.A., Canada, China), by using
the PNEUMA SYSTEM:
1) Dredging of Osaka Harbour - Japan - Osaka Port Authority
A. Operating Data Form
Location Osaka Bay - Port of Osaka Japan
Customer Osaka Port Authority
Period
Performance
trial on 1971
Uninterrupted
dredging operation from 1974 to 1990
Job Description
Dredging
of silty/clayey sediments, highly polluted, with reflow on hopper barges.
Dredging depth 12 m. After a performance trial carried on 1971 with a
Pneuma Pump model 300/60, capacity of 360 cu.m./hour of mixture, installed
on an existing pontoon, the dredging job has been carried out with a Pneuma
Pump model 450/80, capacity of 600 cu.m./hour of mixture, outfitted on
a purpose engineered dredge pontoon manufactured by Sumitomo.
Volume of material dredged Some millions of cu. m.
Content of Solid Material in the Dredge Mixture Up to 90% in volume of sediments in the mixture.
Induced
Turbidity Practically
ZERO
 |
 |
B. Reports and references
The
Japan Dredger Technical Society - n. 82 – July 1972
"Test
Report on dredging by SIRSI* Pneuma System Pumps"
Yasushi Takamura - Manager, Technical Division et al
Port and Harbour Bureau - City of Osaka
quotation
from pag. 10:
".............
the water transparency after the operation decreased by about
20-30 cm. under normal operation……….."
and para. 6 Conclusions:
"............. dredging Hedoro sediments in volume solid content ratio
of
82-95% of natural sedimentary conditions is readily possible with Pneuma
System…….."
The
Japan Port and Harbour Association – Vol. 49 – 8 – 1972
"Hedoro
dredging in Osaka Port area"
Yasushi Takamura - Manager, Technical Division et al
Port and Harbour Bureau - City of Osaka
see
para. 6:
"..........among
other techniques, for dredging Hedoro, that using the Pneuma Pump System may
be considered the most effective and practical. If the above mentioned dredging
technique is used, it should be possible to solve the problems efficiently
without causing any secondary pollution which serves the double purpose of
dealing with anti pollution and land reclamation work simultaneously."
Osaka
Port Authority
"Study
of Solid Dispersion into Aquatic Environment during SIRSI* -Pneuma
Pump Operation - part 1 and 2" - 1973
see
Conclusions :
"it
may be concluded that turbidity value................. during operation.................
was practically ZERO."
The
Japan Dredger Technical_Society - n. 95-September-1974
Operation
Report on Skinkai - The Pneuma Dredge
Shiro Kasajima - Manager 1st Construction Office
Port and Harbour Bureau - City of Osaka
"On
the Dredging Operation for Removal of Bottom Sediment in Osaka Port by the
Pneuma Pump Dredge SHINKAI" - 1986
Shiro
Kasajima - Manager, 1st Construction Office
Port and Harbour Bureau - City
of Osaka.
"The Authority of Osaka City had noticed the excellent performance
of Pneuma Pump System and undertaken the first mud dredging experiment in Japan
with this system, which was introduced by an Italian Company S.I.R.S.I.* in
December 1971. Through this experimental dredging, the suitability of Pneuma
Pump System to the dredging of polluted mud has been well proven.
As part of the pollution control project of the port and harbour, the Bureau
completed the Pneuma Dredger SHINKAI in July 1974 and then organized a dredging
squadron together with the hopper barges that undertaken necessary modifications.
The squadron has been engaged in dredging operations of polluted mud since November
1974 until today".
*
first name of PNEUMA srl
2) PCB Cleanup Operations - Duwamish Waterway - Seattle Harbour - Washington
A.
Operating Data Form
Location
Duwamish Waterway - Seattle Harbour - Washington
- USA
Customer
Seattle District US Corps of Engineers
Period
March
1976
Job Description
|
On
13 September 1974, 260 gallons of PCB's where spilled into Slip 1 of the
Duwamish Waterway, Seattle Harbour - Washington. An emergency removal operation was undertaken by EPA, in which divers utilising small hand-held suction dredged to pump the water, PCB's and contaminated bottom sediments into settling tanks, was undertaken - An estimated 70-90 gallons of the PCB was removed. A Pneuma pump was utilised in March 1976 by the US Corps of Engineers for the first mayor dredging operations undertaken in the United States to remove PCB, obtaining the recovery with exceptionally low turbidity of the 80-90% of the total 250 gallons spilled. |
|
Dredging Plant Pneuma plant model 600/100 - capacity cu.mt/h. 1.000 of mixture, mounted aboard the Corps of Engineers debris boat Puget.
Induced Turbidity "Exceptional low turbidity"
B. Report and References
- PCB Cleanup Operations Duwamish Waterway - Seattle Harbour
- Washington Seattle District Corps of Engineers.
- Monitoring of trace constituents during PCB recovery
dredging operation - Duwamish Waterway - prepared by US Environmental
Protection Agency- Region X - Surveillance and Analysis Division Laboratory
Branch - Washington - Dr. Joseph Blazevich et al - August 1977
3)
Dredging of the Gibraltar Lake - City of Santa barbara - California - U.S.A.
under the supervision of E.P.A. (Enviromental Protection Agency)
A. Operating Data Form
Location
Gibraltar
Lake
Santa
Barbara - California U.S.A.
PHASE I
Customer
City
of Santa Barbara
EPA Clean Lakes Program
Consultant Spencer Engineering - Santa Barbara
Contractor Granite Construction Co. - Watsonville California
Period 1981
Job
Description Dredging, from the water reservoir of Santa Barbara, of silty/clayey
bottom material highly polluted with mercury, without interrupting the water
supply to the city of Santa Barbara.
The dredge mixture reflowed from the bottom ( - 20 m. ) of the lake to the
disposal site at an elevation of 35 m., over the water surface, and at a distance
of 800 m. from the dredging location.
Volume of material dredged 92.000 cu. yard
Dredging Plant Pneuma Pump model 450/80, having an operating capacity of 600 cu.m./hour of mixture
Content
of Solid Material in the Dredged Mixture
Average 40 - 50% in volume, up to 70% of “in situ sediments”
Induced Turbidity NONE
PHASE II
Customer as above
Contractor City of Santa Barbara, after acquisition of the Pneuma Dredge from Granite Construction Co.
Period 1982 - 1986
Job Description As above
Volume
of material dredged 626.000 cu. yard
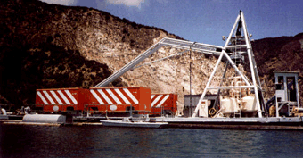 |
 |
B.
Reports and references
Gibraltar Lake Restoration Project - Final Report submitted to U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
prepared
from
The City of Santa Barbara-Public Work Department Water Research Division -
May 1987
quotation
from pag. 53 :
"………
we pumped an average of 700-800 cu.yard slurry per hour with an average velocity
of 7-9 feet per second and an average of 40-50% solids through a distance
of 2300' and 170' of vertical head. At times, the percent solids would go
to approximately 70%……"
and
55:
"
The pump will out-perform the normal dredging methods and is an economical
and efficient method of transporting toxic sediments without disturbance to
the water supplies or environment."
4) Contaminated Sediment Removal Technology Demonstration Program-Great Lake Action Plan - Canadian Government - Environment Canada - Ontario Region.
|
NOTICE Notice is hereby given that the Government of Canada, through Environment Canada, is seeking proposals or expressions of interests for the demonstration of technology suitable for the removal of Great Lakes contaminated sediment. Innovative technologies possessing the capability to excavate, extract or remove contaminated bottom sediments while eliminating adverse environmental effects will be eligible for funding. The objective of this program is to identify technologies by 1994 which are capable of cost-effective removal, handling and pre-treatment of contaminated sediments from the Great Lakes Area of Concern.
|
The Pneuma pump has been chosen, during an international selection between 125 contenders, by the Canadian Government within the context of the
GREAT LAKES ACTION PLAN - CONTAMINATED SEDIMENT REMOVAL TECHNOLOGY DEMONSTRATION ( CSRP)
having the purpose to define the most appropriate system for the dredging of the highly polluted bottoms of the Great Lakes.
The Pneuma Pump has been successfull in achieving the operational performance standards set by the program, notwithstanding the presence of large debris during the performance test carried out in Collingwood Harbour - Ontario - Canada during 1992.
A. Operating Data Form
Location
Collingwood
Harbour
Ontario - Canada
Customer
Ministry of Environment - Environment Canada
Toronto - Canada
Consultant
HSP Inc. Engineering and Environment Scientist
Harva - Ontario
Contractor
Voyageurs Marine Contractors Co. Ltd
Dorion - Quebec
Period
November 1992 - Official Performance Test
November 1993 - Additional Dredging
Job
Description Dredging in the west and east slipways:
- lenght 200 m.
- width 30 m.
- depth 4-6 m.
of silty clay polluted with PCB and metals.
- thickness of sediment to be dredged 0.05 - 1.80 m.
Dredging carried out with a Pneuma Pump model 150/30/R, capacity 150 cu. m./hour
of mixture, lifted by a crane mounted on an existing pontoon of the contractor,
reflowing to the disposal site at a distance of Km 1.2 at the end of the east
breakwater through a PEHD floating pipeline with submerged sections where
crossing ship's ways of the harbour.
Presence of small and large debris, in the dredging area, from yard's construction
activities during the years.
Volume
of material Dredged During performance test (1992) 4.330 cu.m.
During additional dredging (1993) 3.000 cu.m.
Content
of Solid
Material in the Dredged Mixture
Average
30% in volume of solid, where in presence of debries in the dredging area.
Up to 70% in volume of solid, in areas free from debris
Induced Turbidity
WITHIN THE LIMITS required for the Performance Test, notwithstanding the presence of small and larges debris
 |
 |
B. Report and References
Terms of References for the Contaminated Sediments Removal Technologies Demonstration Program - May 1991
Contaminated
Sediment Removal Program - Program Status with a View to the Future - October
1993
Carol
Burchberger - Environmental Protection Canada presented from:
Ian Orchard, Chief
Roger Santiago, Environmental Project Officer
Carol Buchberger, Environmental Project Officer
Innovative
Technologies for the Remediation of Contaminated Sediments - December 1993
Sixth
International Simposium - Santa Barbara - Cal. - USA
Ian Orchard and C. Buchberger - Environment Canada
Using
the burden of evidence approach for sediment management case study Collingwood
Harbour - May 1995
Sediment
remediation 95 - Windsor - Canada
Crail Krantzemberg - Ontario Ministry of Environment and Energy - Toronto
Canada
Approach
to Contaminated Sediment Management through Technology Innovation May 1995
Sediment
remediation ' 95 - Windsor - Canada
Ian Orchard - Environment Canada - Environment Protection Branch, Ontario
Quotations
As a result of the demonstration, it was shown that this technology has proven ability to operate amongst an assortment of different sized debris.
A
comparison of the Pneuma Pump to a conventional cutterhead suction dredge (hydraulic),
shows that the Pneuma Pump is capable of significantly lower concentrations
of total suspended solids during operation.
B. Report and References
 |
 |
| Dredging
of silt in Mackay harbour (Australia)
In
may 2004, Giles Group Australian Environmental Dredging of Mackay carried
out with a new Pneuma dredge 300/60 - VS with vacuum system - capacity
360 cu.mt/h. of mixture the dredging of silt in the Mackay harbour.
Dredging depth 6 mt. with reflow in hopper barges. The pictures show the dredge and the very high content of solid in the mixture.
|